Datasets¶
Data of our view are organized in Datasets. Each Dataset is imported from one of the supported Rulex Studio origins and contain the possible attributes to be linked to our slide/dialog or report widgets.
In the Datasets left panel tab, users can add one or multiple dataset/s to the current view by clicking the Add new dataset icon.
When clicking the Add new dataset icon, the Dataset Import window opens and allows users to proceed with the import and configuration operations.
The import process, starting in the Dataset Import window, begins with a preliminary step which allows users to set the connection type.
The two connections options are:
Saved: the data to import come from an already existing resource, and it is the option set by default.
In this case, users can select the desired resource directly from the Dataset Import window, skipping the custom origin details configuration, where users specify the filesystem or database connection parameters.Custom: the data to import can be used in the current view only.
In this case, before the configuration step users have to configure the custom origin details.
Tip
If users have not defined the saved source yet, they can add one by clicking or hovering over the Plus button, located in the right corner of the Dataset Import window. The available options are:
Then, users will define the data origin. Click on the corresponding link below to check out the different configuration procedures:
At the end of the whole process the imported datasets will appear in the Datasets panel.
If you right-click on one or a series of imported datasets in the Datasets panel, a context menu opens up, and the following options are available:
Delete: it deletes the corresponding datasets from the Datasets panel. This operation is forbidden if one of the attributes is still used in some slide/dialogs or report widgets.
Rename: it allows renaming the selected datasets in the Datasets panel. This operation will silently update attributes connection on slide/dialogs or report widgets where they are used.
Information: it opens the Dataset Information panel where users can get an overview of the dataset origin. The information displayed vary according to the data origin of the dataset. Through this panel it is also possible to modify the origin of an already added table, further information in this section.
Dataset Attributes View¶
Once the user imports one or more datasets in the view, they will be shown in a list. In the Datasets panel, an imported dataset is displayed with a dataset icon, the name of the dataset and a side arrow. The color and the symbol of each dataset icon will change according to the type of dataset origin, as in the following table:
Icon |
Color |
Data origin |
|---|---|---|
Red |
Database |
|
Purple |
Filesystem |
|
Green |
Flow |
By clicking the name of the imported dataset or the arrow icon next to it, the list of attributes contained in the dataset will be displayed.
Users can drag the entire dataset or select an attribute (or more than one by pressing either Ctrl or Shift keys) and drag it into the widgets of the slide, dialog or report to associate them as the input of the considered widget. The effect of this operation differs from widget to widget. Please refer to widgets description for further details.
In the upper right side of the panel, next to the Add new dataset icon, two other icons are present:
Search icon permits to filter the list of Datasets retaining only attributes which include the searched string.
Refresh icon allows the user in edit mode to force the trigger of a data refresh.
Dataset Information Panel¶
After having correctly imported a dataset, users can modify their configuration through the information panel. To access to information panel to change the configuration of a dataset, users need to right-click a dataset in the Dataset panel, and select Information. Once opened, users need to click on the pencil icon in the top right corner of the panel to start editing the configuration options of the imported dataset.
Users can modify the dataset configuration options, but cannot modify the data origin type. For example, once users have imported a dataset from a task in a flow, they can use the information panel and click on the pencil icon to change the task or flow from which the dataset is imported. However, they cannot switch the data origin from flow to database or filesystem.
For databases and remote filesystems, users can switch from a saved source to a custom source and vice versa. When switching from saved to custom source, the information panel is automatically filled with the configuration options previously defined for the saved source.
According to the type of imported dataset, the dataset configuration options to be modified are different. You can find specific options to be modified in the corresponding pages: from flow, from filesystem, from local filesystem, from database.
Dataset Relation¶
This section describes dataset relation, which is how different datasets can be interconnected in Rulex Studio.
A dataset relation involves specific attributes, which can be linked either manually or automatically. When attributes are linked, any operation performed on one attribute is also propagated to the other in the related dataset.
This feature can be managed in the View preferences menu through a specific checkbox, called Use names to construct relations.
When this checkbox is selected, datasets sharing an attribute with the same name are automatically interconnected, meaning that operations applied to that attribute (e.g. filters) are propagated to both datasets.
When it is not selected, no relations between datasets are automatically generated, but they can be configured manually. Full explanation of this operation is available in the corresponding section below.
If the Use names to construct relations checkbox has been selected, this data relation has strong implications when using data filtering and data selection, as the selection or filtering operations are applied on datasets sharing the same attribute name, not only on the selected or filtered on, consequently the displayed data will vary.
For example, when using a Table widget every row index set on the Table generates a row index in the datasets linked to it.
Below an image showing how data selection affects multiple datasets sharing the same attribute names, so the Use names to construct relations option is active.
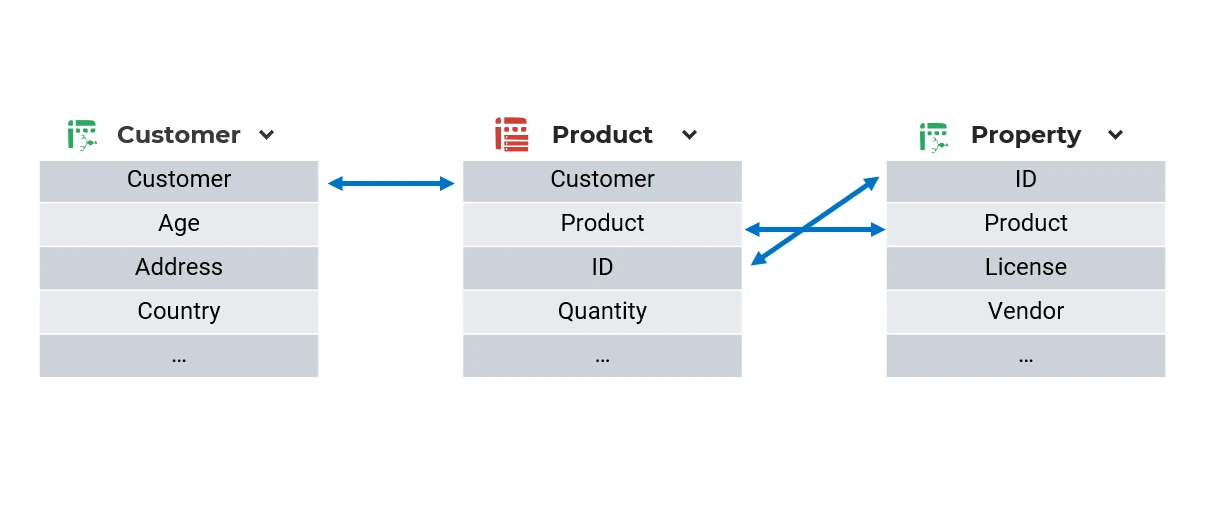
In this image there are three different datasets: Customer, Product, and Property. The Customer and Product datasets both contain the customer attribute, so a selection on the customer attribute also generates a selection on products. The Product and Property datasets both contain the product and ID attributes, so a selection on the product attribute also generates a selection on licenses, and so on.
The same relation can also be established between attributes which don’t have the same name, but are directly chosen by the user through the Use names to construct relations option.
If it is not selected, a new button, called Configure relations, appears in the Datasets tab, providing access to a specific menu where users can manually set up connections between attributes.
:raw-html-m2r:<h3>Table relations</h3>
To open the Table relations window, click on the Configure relations button in the Datasets tab.
In the Table relations window, users can manually define custom relations between different datasets.
Once opened, the Table relations window is empty, and it is divided into three main columns: two on the sides, called Left table and Right table, respectively, and one in the middle, which is the stage where users manually build the relations.
To start building a relation, choose the datasets to be linked from the Left table and Right table drop-down lists. Only tables that were previously imported in the Datasets tab are available for selection.
Once the tables have been chosen, the Relations area appears, where two grey user icons represent the placeholder for the attributes which will be dragged onto them.
To generate a relation, drag the two attributes coming from the two datasets onto the Relations area.
Two more buttons are available in the bottom-left corner of the Table relations window:
the Undo button, which rolls back the last operation performed by reaching the closest saving operation.
the Redo button, which cancels the previous undo operation.
Click APPLY to save the relations, or click CANCEL to close the window without saving changes.
Warning
It is possible to use the Table relations window only if at least two tables have been imported into the view.
Attention
If an attribute name is changed, and the attribute is used in a relation, it is required to create again the relation. The updated name will be displayed in the Left table or in the Right table area, but it will be displayed with its original name in the Relations area, and it will be greyed out. To replace it, users need to right-click onto the greyed attribute and click Delete, then they need to create again the relation by dragging the new attribute onto the Relations area along with the one coming from the other table.
Data Refresh¶
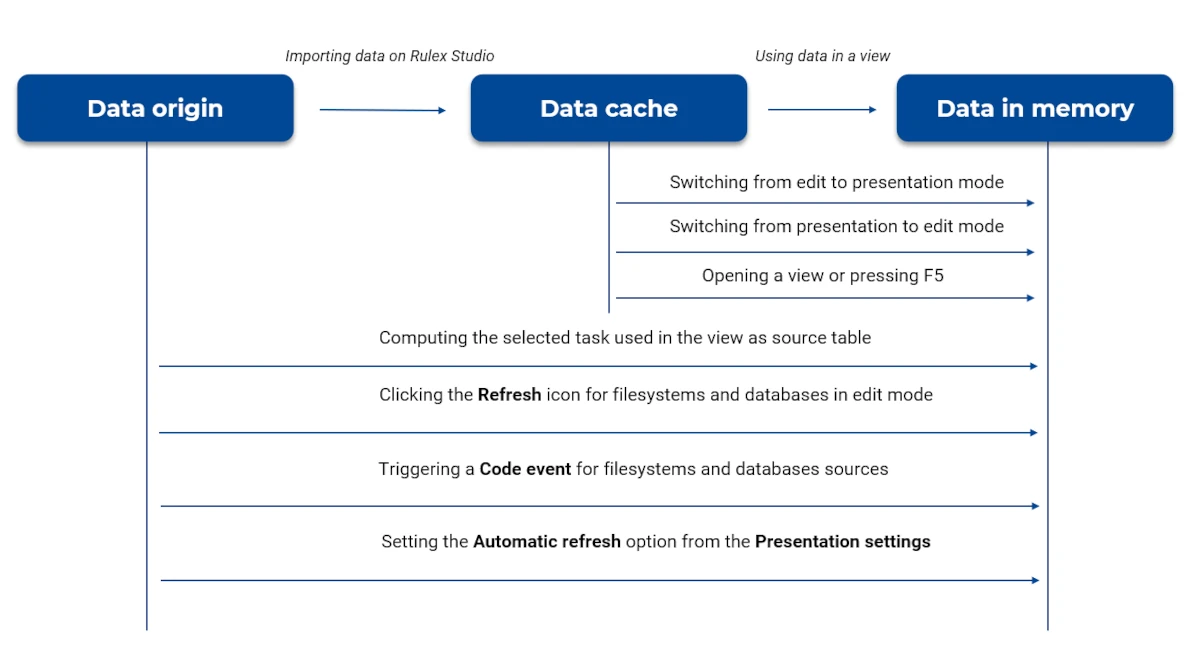
The underlying structure of data transmission in Rulex Studio is divided onto 3 levels:
data origin - it’s the data source (filesystem, database or flow) connected to Rulex Studio used to import datasets.
data cache - it’s data saved on the working database.
data in memory - it’s data used by the view.
Data is transmitted across different levels, this paragraph explains how and when data is updated in each level.
When data is imported into the view, it is synced from the data origin to the data cache. Then, when the data is used in the view, it is synced again from the data cache to memory. Every time users switch from edit mode to presentation mode and vice versa, data is synced from data cache to data in memory. Every time the data cache level changes, the data in memory level is updated as well, and the view displays the modifications. However, in editing mode this data transmission occurs only when the user clicks the Refresh icon in the upper right side of the Datasets pane.
Below you’ll find a list explaining when data is synced from data origin to data in cache, and it varies depending on the working mode and the data source type.
When users are in editing mode the refresh works in the same way for both data imported from Filesystem, database or flow. If some changes are made in the original data, it is necessary a manual refresh to effectively visualize them in your view. To perform a manual refresh you can: click the Refresh icon in the upper right side of the Datasets pane, switch slide or view or even press the F5 key.
- When users are in presentation mode, it is necessary to make a distinction based on the data origin:
For data tables imported from database and filesystem, the changes made in the original data are shown by setting a Refresh event or by defining a refresh timeframe in the Presentation settings menu. Here users can simply select the Automatic refresh checkbox and customize the refresh timeframe in the Refresh time (seconds) box.
For data tables imported from flows, the transmission of the data updates from Rulex Factory to Rulex Studio happens when the task has been computed. Therefore, once the computation has been completed, the data in your view update automatically.
Below you’ll find a picture displaying how data sync from each level.
Dataset GOLD Class Reference¶
Here we present property and methods of the Dataset GOLD class:
- class classes.dataset.Dataset(ref='dataset', id=None, db=None, sessionlike=False, filepath=None, alsodesc=False, onlyinfo=False, tables=None, results=True, loadformat=True)
Base class for data structure in GOLD. Underlying C structure is saved in datarefrec field. An instance of Dataset type can be assigned to the $ symbol to have a shortcut for column retrieval and for method calling. Columns are saved in the C structure and extracted in a parallel GOLD array data when they are used in operation. Extraction operation is triggered by using the $ symbol or through a [] operation on Dataset class.
We are going to indicate as column in this whole file a parameter which may accept $ shortcut or combination of $ shortcut and with GOLD base type parameter which can not. In every parameter with column type, a vector can be inserted as well.
- Property indrow:
possible index of rows to be displayed
- Property modified:
binary vector taking the information about possible alignment between C structure and corresponding extracted column in data field
- Property setstore:
if True the dataset has been modified from its creation.
- Property ndata:
the number of rows
- Property ntot:
the number of columns
- Property currview:
the current model set visualized
- Property view:
a GOLD dictionary storing the information about the different model set applied on this Dataset instance
- Property tab:
a GOLD dictionary in the form {“table_name”: {“indrow”:None, “ndata”:cdata, “order”:i, “modified”:False,”currview”:None, “query_code”:None, “visible”:0, “indcol”:None} to manage multi-table case. To each table name is associated an index of rows, a total number or data, a possible table order, a modified flag, the current model set, the current applied query, a visible flag and a possible index of column displayed.
- Property currlabel:
the current table name in a multi-table case
- Property query_code:
the GOLD code of the current query applied on the Dataset instance
- Property tabsep:
the separator used in $ shortcut to treat multi-table case. Full column name is in the form <table_name><tabsep><column_name>, defaults to !
- Property indcol:
possible index of columns to be displayed
- Property toalign:
flag indicating if the Dataset instance is to be aligned to an internal tab change in the multi-table case
- Property header:
a DataHeaders instance taking all the information about columns
- Property metadata:
a DataHeaders instance taking all the information about metadata, metadata present in Dataset instance are: #data for the number of rows and RowIndex for the possible index of displayed rows.
- Property sessionlike:
if True all dataset operation are connected to an Undo structure to record them and allow undo-redo operations.
- Property formatting:
a GOLD dictionary taking all the formatting rules to applied a conditional formatting style of the Dataset instance
- Property undo:
an Undo class to retain the set of operations (and its undo/redo operations) performed in the case property sessionlike is equal to True
- Property datarefrec:
the underlying C structure connected
- Property data:
a GOLD two-dimensional array representing the GOLD mask for the underlying structure. Columns are populated by using $ shortcut or [] operator on Dataset instance.
- Property databck:
a GOLD two-dimensional array used to store backup needed for undo operations, used only if sessionlike is True
- abs(column)
Function to perform the absolute on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated absolute
- Return type:
vector
- acos(column)
Function to perform the inverse cosine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated inverse cosine
- Return type:
vector
- acosh(column)
Function to perform the hyperbolic inverse cosine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated hyperbolic inverse cosine
- Return type:
vector
- addAttribute(name, type, role, check_existing=True, consres=False, removeundo=True)
Function to add attributes to the Dataset. New attributes will be added at the bottom
- Parameters:
name (vector of text type) – names of the new attributes
type (vector to text type) – types of the new attributes
role (vector of role type) – roles of the new attributes
check_existing (binary) – if True error is raised if one attribute with the same name is already present, defaults to True
conres (binary) – if new attributes need to be added to the attribute subpart or to the result subpart. If True columns are added as results for the Dataset, defaults to False
removeundo (binary) – if True undo operation of attribute addition added just before the current one are removed. Useful to combine subsequent addition in a unique undo operation, defaults to True.
- addMonth(date, nmonth)
Function to add a number of month to a provided date
- Parameters:
date (column) – the provided date
nmonth (column) – the number of month to add
- Returns:
the shifted date
- Return type:
vector of date type
- addQuarter(date, nquarter)
Function to add a number of quarter to a provided date
- Parameters:
date (column) – the provided date
nquarter (column) – the number of quarter to add
- Returns:
the shifted date
- Return type:
vector of date type
- addRow(nrow, view='all')
Function to add a set of new rows at the end of the current Dataset
- Parameters:
nrow (integer) – the number of rows to add
view (text) – the model set view to which new rows needs to be add. One of all, training, test, validation, defaults to all
- addTab(newd, copydata=True, tabname=None)
Function to add a table to a multi-table Dataset instance
- Parameters:
newd (Dataset) – the Dataset instance which contains the information of the new table
copydata (binary) – if True not only columns information are copied in the new tab but also data, defaults to True
tabname (text) – the name of the new table, if None it is taken from field tab of newd. The case newd is not a multi-table Dataset instance is still not implemented, defaults to None.
- addWorkingDays(date, ndays)
Function to add a number of working days to a provided date
- Parameters:
date (column) – the provided date
ndays (column) – the number of working days to add
- Returns:
the shifted date
- Return type:
vector of date type
- addYear(date, nyear)
Function to add a number of year to a provided date
- Parameters:
date (column) – the provided date
nyear (column) – the number of year to add
- Returns:
the shifted date
- Return type:
vector of date type
- align()
Function to force an alignment between the Dataset instance and the underlying C structure
- alignFields(label=None)
Function to change or align the current table in a multi-table Dataset case
- Parameters:
label (text) – the table to align
- anovap(column, attclass, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=True)
Function to perform the anova P between two columns
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column considered in the operation
attclass (column) – the second attribute considered as target
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any column entry
usemissing (binary) – if True None is considered as a possible output value, defaults to True
- Returns:
the evaluated anova P or group of evaluated anova P
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- anovat(column, attclass, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=True)
Function to perform the anova T between two columns
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column considered in the operation
attclass (column) – the second attribute considered as target
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any column entry
usemissing (binary) – if True None is considered as a possible output value, defaults to True
- Returns:
the evaluated anova T or group of evaluated anova T
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- argMax(column, group=None)
Function to compute the index position of the maximum in a column, eventually grouped
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
- Returns:
the index of the maximum or a group of index
- Return type:
integer or group of integers
- argMin(column, group=None)
Function to compute the index position of the minimum in a column, eventually grouped
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
- Returns:
the index of the minimum or a group of index
- Return type:
integer or group of integers
- asin(column)
Function to perform the inverse sine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated inverse sine
- Return type:
vector
- asinh(column)
Function to perform the hyperbolic inverse sine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated hyperbolic inverse sine
- Return type:
vector
- assignView(currview='test')
Function to assign all the current displayed rows to a particular model set
- Parameters:
currview (text) – the new model set to assign. One of all, training, test, validation, defaults to test.
- atan(column)
Function to perform the inverse tangent on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated inverse tangent
- Return type:
vector
- atanh(column)
Function to perform the hyperbolic inverse tangent on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated hyperbolic inverse tangent
- Return type:
vector
- binary(var)
Function to cast a column to binary type
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- breakLoop(condition=True)
Function to break a module loop iteration in the case a condition is True
- Parameters:
condition (binary) – a condition string eventually containing columns
- cast(var, newtype, forced=True)
Function to change the type of a column
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
newtype (text) – the type to cast to
forced (binary) – if True cast of the column is performed even if it leads to a loss of information, defaults to True
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- catNames(indatt, values, separator='-', negate=False)
Function to return as a result for each row the concatenation of the names of the subset of the given columns which presents one of the given values
- Parameters:
indatt (vector of text type or of integers) – the names or the indexes of the selected columns, None for all
values (vector) – the values to check the presence
separator (text) – the separator used to concatenate the column names in the result, defaults to -
negate (binary) – if True names of the columns which does not present any of the listed values are concatenate, defaults to False
- Returns:
a vector composed by the column name concatenation.
- Return type:
vector of text type
- cdf(column, *args, group=None, distr=None, **kwargs)
Function to evaluate the cumulative distribution function of a data column with respect to a particular distribution. Parameters for each distribution are: {“uniform” : [“min”, “max”], “gaussian” : [“mean”, “stdev”], “exponential”: [“beta”, “min”], “gamma”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “beta”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”, “max”], “cauchy”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “tstudent”: [“nu”, “mean”, “stdev”], “logistic”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “weibull”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “lognormal”: [“mean”, “stdev”, “min”], “chisquare”: [“nu”, “min”], “fdistr”: [“nu1”, “nu2”, “min”], “ksdistr”: [], “poisson”: [“lambda”],”binomial”: [“n”, “q”]}
- Parameters:
column (column) – the data column
args (list) – positional arguments used to define the distribution parameters
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
distr (text) – the distribution to use, None for uniform. One of uniform, gaussian, exponential, gamma, beta, cauchy, tstudent, logistic, weibull, lognormal, chisquare, fdistr, ksdistr, poisson, binomial, defaults to None
kwargs (dict) – keyword arguments used to defined the distribution parameters
- Returns:
the cumulative distribution function, eventually grouped
- Return type:
vector or group of continuous
- ceil(column)
Function to perform the ceiling on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated ceiling
- Return type:
vector
- changeAttribute(attribute, field, newvalue=None, oldvalue=None, tab=None, setundo=True)
Function to edit a characteristic of an attribute
- Parameters:
attribute (vector) – the names or the indexes of columns to be modified
field (text) – the characteristic of the column to be modified
newvalue (any) – the value to set, defaults to None
oldvalue (any) – if requested the value present which needs to be substituted, defaults to None
tab (text) – the table name in a multi-table Dataset case, None for the current one, defaults to None
setundo (binary) – if True the operation is recorded in the Undo class if available, defaults to True
- changeCurrency(var, currency, applychange=False)
Function to change the currency of a currency unit
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
currency (text) – the new currency unit. One of dollar, euro
applychange (binary) – if True the value will be change according to current change ratio. NOT IMPLEMENTED YET, defaults to False
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- changeSessionlike(sessionlike=None)
Function to modify the property sessionlike
- Parameters:
sessionlike (binary) – if True all dataset operation are connected to an Undo structure to record them and allow undo-redo operations
- checkAttributes(attribute, field='all')
Function to control visibility of a set of attributes
- Parameters:
attributes (integer or vector of integers) – the attribute visibility, use 1 to set it visible, 0 to set it as hidden
field (text) – keyword used to modify a subset of attributes without providing the full list, all for all the columns, attribute for all attribute columns and results for only result columns, defaults to all
- Returns:
a dictionary with two keys, results and attributes, and values 0 if all the result/attribute columns are hidden, 1 if all the result/attribute columns are visible, 2 in any mixed situation
- Return type:
dict
- checkColumnPresent(listcol)
Function to control if a vector of attribute names is present in the Dataset
- Parameters:
listcol (vector of text type) – the attribute names to search for
- Returns:
a vector of True if the column is present, False otherwise
- Return type:
vector of binaries
- chisquare(column1, column2, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=True)
Function to perform the chi squared between two columns
- Parameters:
column1 (column) – the first column considered in the operation
column2 (column) – the second column considered in the operation
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any column entry
usemissing (binary) – if True None is considered as a possible output value, defaults to True
- Returns:
the evaluated chi squared or group of evaluated chi squared
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- chisquarep(column1, column2, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=True)
Function to perform the chi squared P-value between two columns
- Parameters:
column1 (column) – the first column considered in the operation
column2 (column) – the second column considered in the operation
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any column entry
usemissing (binary) – if True None is considered as a possible output value, defaults to True
- Returns:
the evaluated chi squared P-value or group of evaluated chi squared P-value
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- clear(label=None, keepcolumn=True)
Function to erase all the rows in a selected table
- Parameters:
label (text) – the table name in a multi-table Dataset case, None for the current one, defaults to None
- cohenk(column1, column2, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=True)
Function to perform the cohenk between two columns
- Parameters:
column1 (column) – the first column considered in the operation
column2 (column) – the second column considered in the operation
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any column entry
usemissing (binary) – if True None is considered as a possible output value, defaults to True
- Returns:
the evaluated cohenk or group of evaluated cohenk
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- computeBivarStat(sheetres, var1, var2, stats, nquantile=0, contval=False, usetarget=False, targetcond=None, postest=None, usemissing=False)
Function to compute bivariate statistic for a column and store it into a Sheetset instance
- Parameters:
sheetres (Sheetset or # shortcut) – a Sheetset instance where to store the result
var1 (column) – the first column of the Dataset considered
var2 (column) – the second column of the Dataset considered
stats (vector of text type) – the statistic to compute
nquantile (integer) – the number of quantiles (used by some statistics), defaults to 0
contval (binary) – if False compute statistics are casted to integer if the original column was integer, defaults to False
usetarget (binary) – if True the second variable is used as target for the statistic test, defaults to False
targetcond (binary) – FIXME, defaults to None
postest (binary) – FIXME, defaults to None
usemissing (binary) – if True the None value is counted as a distinct value, defaults to False
- computeUnivarStat(sheetres, var, stats, nquantile=0, contval=False)
Function to compute univariate statistic for a column and store it into a Sheetset instance
- Parameters:
sheetres (Sheetset or # shortcut) – a Sheetset instance where to store the result
var (column) – the column of the Dataset considered
stats (vector of text type) – the statistic to compute
nquantile (integer) – the number of quantiles (used by some statistics), defaults to 0
contval (binary) – if False compute statistics are casted to integer if the original column was integer, defaults to False
- concatenate(ds2, cattype='outer', byname='name', checksize=False)
Function to concatenate two Dataset instances. Concatenation is made in-place by substitution of the current Dataset instance with the concatenation of the two.
- Parameters:
ds2 (Dataset) – the second Dataset instance to concatenate
cattype (text) – the type of concatenation to perform, one of inner or outer, defaults to outer
byname (text) – the type of column identification to perform, one of name (columns with the same name are matched) or position (columns with the same index are matched), defaults to name
checksize – if True Dataset C structure is converted to take the major amount of data, if False it is supposed to be already prepared for the concatenation, defaults to False
- connComp(son, group=None)
Function to associate in a graph to any connected subgraph an increasing integer
- Parameters:
parent (column) – parent column defining the graph
child (column) – child column defining the graph
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
- Returns:
the vector or the group of vectors of indexes associated to the connected subgraphs
- Return type:
vector or group of integers
- continuous(var)
Function to cast a column to continuous type
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- cos(column)
Function to perform the cosine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated cosine
- Return type:
vector
- cosh(column)
Function to perform the hyperbolic cosine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated hyperbolic cosine
- Return type:
vector
- count(group=None)
Function to count the number of rows of a Dataset
- Parameters:
group (column) – columns on which perform a group operation to count the number of values of each group, defaults to None
- Returns:
the number of rows or a group of the number of values
- Return type:
integer or group
- countIf(condition, group=None)
Function to count the number of rows fullfilling a particular condition
- Parameters:
condition (text) – a condition string
group (column) – columns on which perform a group operation to count the number of values of each group, defaults to None
- Returns:
the number of rows or a group with the number of values
- Return type:
integer or group
- covariance(column1, column2, group=None, weights=None)
Function to perform the covariance between two columns
- Parameters:
column1 (column) – the first column considered in the operation
column2 (column) – the second column considered in the operation
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any column entry
- Returns:
the evaluated covariance or group of evaluated covariance
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- cumMax(column, group=None, weights=None)
Function to compute the cumulative maximum on a column, eventually grouped and weighted
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – NOT IMPLEMENTED YET a column to be used as weight for the original column. Each row will be multiplied for the corresponding weight before performing the cumulative operation.
- Returns:
the cumulative maximum or a group of cumulative maximum
- Return type:
any or group
- cumMin(column, group=None, weights=None)
Function to compute the cumulative minimum on a column, eventually grouped and weighted
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – NOT IMPLEMENTED YET a column to be used as weight for the original column. Each row will be multiplied for the corresponding weight before performing the cumulative operation.
- Returns:
the cumulative minimum or a group of cumulative minimum
- Return type:
any or group
- cumProd(column, group=None, weights=None)
Function to compute the cumulative product on a column, eventually grouped and weighted
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – NOT IMPLEMENTED YET a column to be used as weight for the original column. Each row will be multiplied for the corresponding weight before performing the cumulative operation.
- Returns:
the cumulative product or a group of cumulative product
- Return type:
any or group
- cumSum(column, group=None, weights=None, minlimit=None, maxlimit=None, threshold=None)
Function to compute the cumulative sum on a column, eventually grouped and weighted
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – A column to be used as weight for the original column. Each row will be multiplied for the corresponding weight before performing the cumulative operation.
minlimit (integer or float) – the minimum limit of the cumulative sum. If this limit is reached cumulative sum is set to this value, defaults to None.
maxlimit (integer or float) – the maximum limit of the cumulative sum. If this limit is reached cumulative sum is set to this value, defaults to None.
threshold (integer or float) – if not None the value to restart to if maxlimit or minlimit are reached, defaults to None
- Returns:
the cumulative sum or a group of cumulative sum
- Return type:
any or group
- currency(var, currency=None)
Function to cast a column to currency type
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
currency – the currency unit to set. One of dollar, euro. Use None to nocurrency, defaults to None
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- datasetToHeader()
Function to switch back from Header visualization to Data visualization In Data visualization (default one), Dataset instance shows data column and operate on data which are the rows of the dataset In Header visualization, Dataset instance shows an attribute for each row and operate on them acting on column which are fixed. Columns in header visualization are: [“name”, “type”, “role”, “ignore”, “label”, “dist”, “norm”, “miss”, “avg”, “min”, “max”, “stdev”]
- date(year, month=None, day=None)
Function to construct or convert a date column
- Parameters:
year (column) – a integer column representing the year of the desired constructed date, or a month, week, quarter, datetime or text column to be casted to date, defaults to None
month (column) – in case year is an integer, the month integer necessary to construct the date, defaults to None
day (column) – in case year is an integer, the day integer necessary to construct the date, defaults to None
- Returns:
the constructed date vector
- Return type:
vector of dates
- datetime(date, time=None)
Function to construct or convert a dateime column
- Parameters:
date (column) – a date column representing the date of the desired constructed datetime, or a month, week, quarter, date, time or text column to be casted to datetime, defaults to None
time (column) – in case date is an date, the time column necessary to construct the datetime, defaults to None
- Returns:
the constructed datetime vector
- Return type:
vector of datetimes
- day(date)
Function to extract the day of a given date column as a number from 1 to possibly 31
- Parameters:
date (column) – a date column
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted day
- Return type:
vector of integers
- decideType(column)
Function to force a smart type recognition on a column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to recognize
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- discretize(column, nvalue=2, cutoffs=None, mode='ef', rank=False, quantile=False, min=None, max=None)
Function to perform a discretization on a column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to discretize
nvalue (integer) – the number of values to create, meaning the cutoffs will be nvalue-1, defaults to 2
cutoffs (vector of continuous type) – a possible vector of cutoffs. If present the function only applies the cutoffs to discretize values in the column, defaults to None
mode (text) – type of algorithm used to create the cutoffs. Possible values are: ef (Equal frequency) or ew (Equal width), defaults to ef
rank (binary) – if True FIXME, defaults to False
quantile (continuous) – FIXME, defaults to None
min (any) – the provided minimum of the column, None to evaluate it from data, defaults to None
max (any) – the provided maximum of the column, None to evaluate it from data, defaults to None
- Returns:
a discretize vector
- Return type:
vector
- distance(column1, column2, method)
Function to evaluate the distance between two columns
- Parameters:
column1 (column) – the first column
column2 – the second column
method (text) – the distance method to be used
- Rtype column2:
column
- Returns:
the vector with the distances
- Return type:
vector of integers
- distinct(column, group=None, usemissing=False)
Function to retrieve the number of distinct element in a column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to be analyzed
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
usemissing (binary) – if True the None value is counted as a distinct value, defaults to False
- Returns:
the number of distinct values or a group of numbers of distinct values
- Return type:
integer or group of integers
- divisors(column, separator='-')
Function to evaluate the minimum common multiple of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column to be considered as input of the factorization.
separator (text) – the separator to be used to concatenate divisors, defaults to -
- Returns:
the text concatenation for each row of the divisors of the entering number
- Return type:
text
- editCell(indatt, indrow, newvalue, testtype=True, tab=None, indrelative=False, allrange=False)
Function to edit a rectangle of data with a new value
- Parameters:
indatt (vector of integers) – vector of the absolute column positions to edit
indrow (vector of integers) – vector of absolute row positions to edit
testtype – if True editing is performed only if does not require any column cast, defaults to True
testtype – binary
tab (text) – the table name in a multi-table Dataset case, None for the current one, defaults to None
indrelative (binary) – if True indatt and indrow are considered as relative to displayed rows and not absolute, defaults to False
allrange – if True indrow is considered as the entire indrow to edit and not as a range, defaults to False
- entropy(column, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=False, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the entropy of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns entropy is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the entropy of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the entropy row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated entropy is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- enum(columns=None)
Function to assign an incremental number to the rows of a Dataset
- Parameters:
columns (column) – one or more columns to force the algorithm to enumerate inside the groups created by the selected columns, defaults to None
- Returns:
a vector or a group of vectors containing the enumeration of their internal rows
- Return type:
vector or group of integers
- enumRuns(column)
Function to return an incremental index in any group produced by a call of the runs function
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
a vector of incremental index
- Return type:
vector of integers
- error(condition=True)
Function to raise an error with a certain code and message
- Parameters:
message (text) – the error message, defaults to None
condition (binary) – the condition to check to determine whether error should be raised, defaults to True
- Raises:
Error – an error with message ‘message’
- errorGold(message, code=9020)
Function to raise an error if a provided condition is True
- Parameters:
condition (binary) – a condition string eventually containing columns
message (text) – the message to sent in case of error
code (integer) – the code error to raise, defaults to 9020
- Raises:
Error with code code and message message if condition is True
- eval(code, iseval=True)
Function to evaluate a GOLD code
- Parameters:
code (text) – the text code to eval
iseval (binary) – if True the result of the evaluation is returned by eval function, defaults to True
- Returns:
if iseval is True the result of the evaluation
- Return type:
any
- evalStyleFormat(formatting=None, style=None, rowstyle=None, spanning=None, cleanstyle=False, cleanformat=False, storeformat=False, aligndataset=False, whichformat=None)
Function to evaluate the styling of a Dataset
- Parameters:
formatting (dict) – the dictionary containing the formatting rules for the conditional formatting. The form is {<column name>: [{single rule dictionary},…], …}, defaults to None
style (dict) – the dictionary containing various column style. The form is {<column name>: <column style>, …}, defaults to None
rowstyle (dict) – the dictionary containing variaous row style rules. The form is {<condition string>: <row style>, …}, defaults to None
spanning (dict) – the dictionary containing various columna and row spanning rule. The form is {“column”: {<column name>: <row spanning rule>, …}, “row”: {<condition string>: <column spanning rule>, …}}, defaults to None
cleanstyle (binary) – if True all styling are erased before applying the evaluation, defaults to False
cleanformat (binary) – if True all conditional rule effects are erased before applying the evaluation, defaults to False
storeformat (binary) – if True a formatting field is store to save styling rule for future use, defaults to False
aligndataset (binary) – if True a method align is called before the evaluation to guarantee the alignment between the GOLD class and the underlying C structure, defaults to False
whichformat (text) – select which of the three different formatting origin (row, column, formatting) you want to evaluate, None for all, defaults to None
- exp(column)
Function to perform the exponential on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated exponential
- Return type:
vector
- export(options, destination, giveerror=True)
Function to export on file or Database the current Dataset
- Parameters:
options (dict) – dictionary of options controlling the export operation
destination (text) – destination type of the export, one of filesystem, database or local
giveerror (binary) – if True error is raised in case of export error, otherwise error is silently dropped, defaults to True
- extractTabDataset(tab, ndata=None, columns=None)
Function to create a new Dataset instance with only one of the table of the original multi-table Dataset
- Parameters:
tab (text) – the selecte table
ndata (integer) – the number of data to copy, None for all, defaults to None
columns (vector of text type) – a vector of column names to copy in the resulting Dataset only a subset of columns, None for all, defaults to None
- Returns:
a new Dataset instance with the extracted table
- Return type:
Dataset
- fact(column)
Function to perform the factorial on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated factorial
- Return type:
vector
- factorize(column, mode='combined', separator='-')
Function to evaluate the minimum common multiple of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column to be considered as input of the factorization.
mode (text) – the form of the result, combined will return each prime factor elevated to its maximum exponent, prime will return only prime factor, exponent will return only the exponent of the prime factors, defaults to combined
separator (text) – the separator to be used to concatenate prime factors, defaults to -
- Returns:
the text concatenation for each row of the prime factors of the entering number
- Return type:
text
- fillDown(column, group=None, fillall=False)
Function to fill the None values in a column present below with the nearest value
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
fillall (binary) – if True a subsequent fillUp function is call on the same column, defaults to False
- Returns:
the filled vector or group of filled vector
- Return type:
vector or group
- fillLinear(column, group=None)
Function to fill the None values in a column present below with a linear interpolation between the two nearest values
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
- Returns:
the filled vector or group of filled vector
- Return type:
vector or group
- fillUp(column, group=None, fillall=False)
Function to fill the None values in a column present above with the nearest value
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
fillall (binary) – if True a subsequent fillDown function is call on the same column, defaults to False
- Returns:
the filled vector or group of filled vector
- Return type:
vector or group
- filter(condition, useindrow=False, store=True)
Function to perform a filter query
- Parameters:
condition (text or Ruleset) – condition string or Ruleset instance containing the filter query to apply
useindrow (binary) – if True the resulting indrow is merged with a previous present indrow in the Dataset, defaults to False
store (binary) – if True, resulting indrow will substitute the property indrow of the Dataset instance, otherwise it is returned, defaults to True
- Returns:
if store parameter is False, the resulting indrow is returned
- Return type:
vector of integers
- find(column, value, binary=True, ischarlist=False, charpos=0)
Function to search a substring inside the texts of a column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column of text type on which perform the operation
value (text) – the substring to search for
ischarlist (binary) – if True the value is considered as a list of chars and each char is searched separately, defaults to False
charpos (integer) – if different from 0, the position of the starting point of the charpos-th occurrence of the substring is returned, otherwise a binary True/False stating if the substring is present or not, defaults to 0
- Returns:
an integer position if charpos is different from 0 or a binary if charpos is 0
- Return type:
vector of integers or binaries
- fit(column, *args, group=None, distr=None, method=None, maxit=None, tol=None, **kwargs)
Function to produce a fit vector obtaining by fitting a data column, eventually grouped with a given distribution
- Parameters:
column (column) – the data column to fit
args (list) – positional arguments used to define the distribution parameters
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
distr (text) – the distribution to use, None for uniform. One of uniform, gaussian, exponential, gamma, beta, cauchy, tstudent, logistic, weibull, lognormal, chisquare, fdistr, ksdistr, poisson, binomial, defaults to None
method (text) – the fit method to use. One of FIXME, defaults to None
maxit (integer) – the maximum number of iteration to perform the fit, None for no limit, defaults to None
tol (continuous) – the maximum tolerance acceptable for the fit, None for any tolerance, defaults to None
kwargs (dict) – keyword arguments used to defined the distribution parameters
- Returns:
the fitted vector
- Return type:
vector
- floor(column)
Function to perform the floor on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated floor
- Return type:
vector
- gcd(column, group=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the greatest common divisor of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns greatest common divisor is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the greatest common divisor of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the greatest common divisor row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated greatest common divisor is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- get(label)
Function to get the information about the table with name label in a multi-table Dataset case
- Parameters:
label (text) – the name of the table to get
- Returns:
the information about table
- Return type:
dict
- getAttField(name_attr, field, link=False, frombackup=False, label=None, withraise=True)
Function to retrieve the information about one characteristic on an attribute
- Parameters:
name_attr (text) – the name of the attribute to consider
field (text) – the characteristic to inspect
link (binary) – FIXME
frombackup (binary) – if True ignore the eventual query active on the Dataset instance, defaults to False
label (text) – the table name in multi-table Dataset case
withraise (binary) – if True an error is raised if the attribute name given is not present in the Dataset instance, defaults to True
- Returns:
attribute information
- Return type:
any
- getAttInfo(list_att, stats=False, properties=False)
Function to obtain attribute information of a list of attributes Standard information are: table, name, type, role containing the table name in multi-table Dataset case, the attribute name, the attribute type and the attribute role
- Parameters:
list_att (vector of text type) – the attribute names of the column to analyze
stats (binary) – if True extra information about mean, min, max and stdev for ordered column, number of missing and number of distinct values for nominal column is added, defaults to False
properties (binary) – if True extra information about column ignored or treated as label, column distribution and normalization is added, defaults to False
- Returns:
a dictionary with key the attribute names and values the information about each attribute
- Return type:
dict
- getAttInfoPanel(list_att=None)
Function to obtain the whole list of attribute characteristic: description: last formula applied on the column type: column type ignore: if the column is ignored label: if the column is considered a label column for clustering operation role: role of the column (input, output…) dist: distribution used in discretizing column for machine learning algorithms norm: normalization used in discretizing column for machine learning algorithms weight: weight used for column values in model applying miss: value considered as missing for the column avg: the mean of the column min: the minimum of the column max: the maximum of the column stdev: the standard deviation of the column
- Parameters:
list_att (vector of text type) – the attribute names of the column to analyze
- Returns:
a dictionary with key the attribute names and values the information about each attribute
- Return type:
dict
- getCaseSens(tab)
Function to obtain the case sensitivity of a Dataset instance
- Parameters:
tab (text) – the table to test in multi-table case
- Returns:
the case sensitive of the table
- Return type:
binary
- getColumn(attr)
Function to obtain as vector the column pointed by a given attribute name
- Parameters:
attr (text) – the column to extract
- Returns:
the column vector
- Return type:
vector
- getIndFilter(indexes, prefix='', query=None, order=None, ascending=True)
Function to get the indexes of the column fullfilling a certain condition
- Parameters:
prefix (text) – a possible extra prefix
query (dict) – the matching criteria expressed as GOLD dictionary with the following key: - filterCriterion which assumes one of the following values (match, startswith, endswith, includes) - text equal to the matching string - words flag to force the matching string to match the whole word - caseSens flag to control if match has to be case-sensitive
order (text) – a string to force the output index to be ordered according to one criteria: name, type, role, ignored
ascending (binary) – if True the order imposed by order parameter is considered as ascending, descending otherwise, defaults to True
- Returns:
the indexes of the column fullfilling the criterium
- Return type:
vector of integers
- getInfo(tablabel=None)
Function to get base information about a table in the multi-table Dataset case
- Parameters:
tablabel (text) – the table name, None means current one, defaults to None
- Returns:
a dictionary with the following keys: - ndata: the number of data - order: the order of the table in the multi-table set - set: the model set view currently applied, if any - nindcol: the number of columns displayed - nres: the number of result columns - nattr: the number of attribute columns - nindrow: the number of rows displayed
- Return type:
dict
- getMemoryInfo()
Function to obtain an estimate about the memory committed by the current Dataset instance
- Returns:
the memory used (in MB)
- Return type:
continuous
- getMultiAttributesField(index_attr, field='type')
Same as GetAttField but for a subset of attributes
- Parameters:
index_attr (vector of integers) – the indexes of the considered attribute
field (text) – the characteristic to inspect, defaults to type
- Returns:
a dictionary with keys the attribute names and values the chosen characteristic for each attribute
- Return type:
dict
- getNumAttributes(tab=None)
Function to obtain the number of attributes
- Parameters:
tab (text) – the table name in the multi-table Dataset case, defaults to None
- Returns:
the number of attributes
- Return type:
integer
- getRect(indcol, col, indrow, row, label=None, filter_att=None, group_att=None, apply_att=None, sort_att=None, pending_att=None, formula_att=None, useindrow=True, useindcol=True)
Function to get the information about a rectangle of data
- Parameters:
indcol (vector of integers) – the index of the columns to be considered
col (integer) – number of columns to be considered
indrow (vector of integers) – the index of the rows to be considered
row (integer) – number of rows to be considered
label (text) – the table name in a multi-table Dataset case, None for the current one, defaults to None
filter_att (vector of text type) – vector of attributes on which a filter query is active, defaults to None
group_att (vector of text type) – vector of attributes on which a group query is active, defaults to None
apply_att (vector of text type) – vector of attributes on which a apply query is active, defaults to None
sort_att (vector of text type) – vector of attributes on which a sort query is active, defaults to None
useindrow (binary) – if True indrow parameter rows are relative to only displayed rows, otherwise they are treated as absolute with respect to the full Dataset, defaults to True
- Returns:
a JSON string containing information about the selected rectangle
- Return type:
text
- getRows(index)
Function to derive from a column a vector containing only the rows pointed by the provided index
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column (meaning the result of a $ shortcut or [] Dataset override operator)
index (vector of integers) – a vector of indexes to selct a set of rows
- Returns:
the selected rows
- Return type:
vector
- getTabIndex(tab, columns=None)
Function to get column indexes in multi-table Dataset case
- Parameters:
tab (text) – the table name
columns (vector of text type) – an eventual column names vector to select a subset of columns we want to retrieve the index, defaults to None
- Returns:
the column indexes
- Return type:
vector of integers
- gini(column, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=False)
Function to perform the gini index of a column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any var object entry
usemissing (binary) – if True None is considered as a possible output value, defaults to False
- Returns:
the gini index or group of gini indexes, expressed as a continuous number between 0 and 1
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- group(group, expand=False, store=True)
Function to perform a group query
- Parameters:
group (list) – list of column names to be considered
expand (binary) – if False property indrow of the Dataset instance is modified to select only the first row of each group, defaults to False
- head(column, nchar)
Function to take the first n characters of each text inside the provided column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column on which perform the head operation
nchar (integer) – the number of characters to take
- Returns:
the vector composed by cut texts
- Return type:
vector of text type
- headerToDataset(withvalues=False)
Function to switch Dataset instance visualization: Data visualization to Header visualization In Data visualization (default one), Dataset instance shows data column and operate on data which are the rows of the dataset In Header visualization, Dataset instance shows an attribute for each row and operate on them acting on column which are fixed. Columns in header visualization are: [“name”, “type”, “role”, “ignore”, “label”, “dist”, “norm”, “miss”, “avg”, “min”, “max”, “stdev”]
- Parameters:
withvalues (binary) – if True two extra column “values” and “weights” are added containing the values of each attribute and the weight associated to each value, defaults to False
- hour(time)
Function to extract the hour of a given datetime or time column
- Parameters:
time (column) – a datetime or time column
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted hour
- Return type:
vector of integers
- ifNone(var, condition, iftrue)
Function to apply the condition only if the original value is None and put the iftrue values if the condition is True
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to consider
condition (column) – the condition to evaluate for None values
iftrue (column) – value to be inserted in substitution of None if the condition is verified.
- Returns:
the vector corrected
- Return type:
vector
- ifelse(condition, iftrue, iffalse)
Function to perform an inline condition
- Parameters:
condition (column) – the binary condition to be evaluated
iftrue (column) – value to be returned if the condition for the current element is True
iffalse (column) – value to be returned if the condition for the current element is False
- Returns:
the merged object with the value of iftrue in all the position where condition is evaluated as True and the value of iffalse elsewhere.
- Return type:
vector
- imputeMissing(attribute, value)
Function to impute missing in a particular value of an attribute
- Parameters:
attribute (vector) – the names or the indexes of columns to be modified
value (any) – the value considered
- inIqr(column, coeff=1.5, weights=None, mult=None)
Function to perform the interquartile range of an column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
coeff (continuous) – the coefficient used for the range evaluation, defaults to 1.5
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any var object entry
mult (column) – NOT IMPLEMENTED YET a column to consider any var object entry as replicated the corresponding value present in mult times
usemissing (binary) – if True None is considered as a possible output value, defaults to False
- Returns:
the interquartile range, expressed as a continuous number between 0 and 1
- Return type:
continuous
- indApply(vect, ind)
Function to apply an index on a column.
- Parameters:
vect (column) – the column on which apply the index
ind (column) – the index to be applied
- Returns:
the vector resulting of the apply
- Return type:
vector
- insertAttributes(names, types, roles, check_existing=True, index=None, target=None, nattr=None, before=False, tab=None)
Function to insert attributes into the Dataset
- Parameters:
names (vector of text type) – names of the new attributes
types (vector to text type) – types of the new attributes
roles (vector of role type) – roles of the new attributes
check_existing (binary) – if True error is raised if one attribute with the same name is already present, defaults to True
index (vector of indexes) – the indexes of the position where to insert the new columns, defaults to None
target (text) – the name of the attrbute where to insert the new columns before or after it, defaults to None
nattr (integer) – impose the number of attributes. If the column using index is inserted after this number it is treated as result for the current Dataset.
before (binary) – if True in connection with target parameter insert the new columns before the target column, after otherwise, default to False
tab (text) – the table name in a multi-table Dataset case, None for the current one, defaults to None
- integer(var)
Function to cast a column to integer type
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- invcdf(column, *args, group=None, distr=None, **kwargs)
Function to evaluate the inverse cumulative distribution function of a data column with respect to a particular distribution. Parameters for each distribution are: {“uniform” : [“min”, “max”], “gaussian” : [“mean”, “stdev”], “exponential”: [“beta”, “min”], “gamma”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “beta”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”, “max”], “cauchy”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “tstudent”: [“nu”, “mean”, “stdev”], “logistic”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “weibull”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “lognormal”: [“mean”, “stdev”, “min”], “chisquare”: [“nu”, “min”], “fdistr”: [“nu1”, “nu2”, “min”], “ksdistr”: [], “poisson”: [“lambda”],”binomial”: [“n”, “q”]}
- Parameters:
column (column) – the data column
args (list) – positional arguments used to define the distribution parameters
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
distr (text) – the distribution to use, None for uniform. One of uniform, gaussian, exponential, gamma, beta, cauchy, tstudent, logistic, weibull, lognormal, chisquare, fdistr, ksdistr, poisson, binomial, defaults to None
kwargs (dict) – keyword arguments used to defined the distribution parameters
- Returns:
the probability distribution function, eventually grouped
- Return type:
vector or group of continuous
- isAttribute(name, binary=True)
Function to state if a name is a name of a column of the current Dataset instance
- Parameters:
name (text) – the name to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the name is a real column name, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isDate(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of date type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of date type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isDatetime(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of datetime type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of datetime type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isFloat(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of continuous type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of continuous type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isInteger(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of integer type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of integer type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isMonth(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of month type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of month type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isPrefix(column, value, binary=True)
Function to establish if a text starts with a given substring
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column of text type to analyze
value (text) – the string to test
- Returns:
a True/False vector
- Return type:
binary or vector of binaries
- isQuarter(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of quarter type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of quarter type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isSuffix(column, value, binary=True)
Function to establish if a text ends with a given substring
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column of text type to analyze
value (text) – the string to test
- Returns:
a True/False vector
- Return type:
binary or vector of binaries
- isTime(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of time type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of time type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isType(string, type, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of a particular type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
type (text) – the type to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of the selected type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isWeek(string, binary=True)
Function to state if a column is of week type
- Parameters:
string (any) – the column to test
binary (binary) – if True the result is returned as binary, otherwise as integer 0,1, defaults to True
- Returns:
True if the column is of week type, False otherwise
- Return type:
binary
- isWord(string, substring, delimiter=' ', binary=True)
Function to state if a substring is present in a given text as a word, meaning with a particular delimiter before and after
- Parameters:
string (column) – a column of text type to analyze
substring (text) – the substring to search for
delimiter (text) – the delimiter to be found before and after to state the found substring is in fact a word, defaults to standard space
binary (binary) – if True a standard binary is returned, otherwise an integer 0/1 for backward compatibility, defaults to True
- Returns:
a True/False or 0/1 with the searched answer
- Return type:
binary or integer or vector of binaries or vector of integers
- join(ds2, jointype='inner', mergetype='nofill', misspolicy='normal', byname=1, checknames=True)
Function to join two Dataset instances. Jon is made in-place by substitution of the current Dataset instance with the joined version of the two.
- Parameters:
ds2 (Dataset) – the second Dataset instance to join
jointype (text) – the type of join to perform, one of inner, louter, router, outer, lcomplement, rcomplement or complement, defaults to inner
mergetype (text) – option to fill missing value using values of the other dataset. One of nofill, left, right, defaults to nofill
misspolicy (text) – option to control how to treat in join comparison missing values. One of normal, always, never, defaults to normal
byname (binary) – the type of column identification to perform, identified by 1 (columns with the same name are matched) or 0 (columns with the same index are matched), defaults to 1
checknames (binary) – if True column addition is checked against the presence of column with the same name, if False user is accounted for this check. If the flag is False and column with the same name will be present, Dataset instance results corrupted, defaults to True
- lcm(column, group=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the least common multiple of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns least common multiple is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the least common multiple of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the least common multiple row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated minimum common multiple is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- leaf(son, group=None, whichpath='min', separator='-', weights=None, operator='sum')
Function to evaluate the leafs of a graph
- Parameters:
parent (column) – parent column defining the graph
child (column) – child column defining the graph
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
whichpath (text) – the leaf searched, min to obtain the nearest leaf, max to obtain the further away leaf, all to obtain all the leafs connected by a separator, defaults to min
separator (text) – in case whichpath is all, the separator used to concatenate different leafs, defaults to -
weights (column) – possible weights column to associate to each node of the graph, defaults to None
operator (text) – the type of operation to use in considering weights of connected nodes; possible values are sum or prod, defaults to sum
- Returns:
the vector or the group formed by the evaluated leafs
- Return type:
vector or group
- leafDistance(son, group=None, whichpath='min', separator='-', weights=None, operator='sum')
Function to evaluate distance from the leafs of a graph
- Parameters:
parent (column) – parent column defining the graph
child (column) – child column defining the graph
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
whichpath (text) – the leaf considered in distance evaluation, min to obtain the nearest leaf, max to obtain the further away leaf, all to evaluate the distance with respect to all the leafs and to connect the numbers by using a separator, defaults to min
separator (text) – in case whichpath is all, the separator used to concatenate different leaf distances, defaults to -
weights (column) – possible weights column to associate to each node of the graph, defaults to None
operator (text) – the type of operation to use in considering weights of connected nodes; possible values are sum or prod, defaults to sum
- Returns:
the vector or group formed by the evaluated distances, eventually separator connected
- Return type:
vector or group of continuous, integer or text type
- len(column)
Function to return the length of a column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to test
- Returns:
the number of rows
- Return type:
integer
- list()
List table information
- Returns:
GOLD dictionary of table information in multi-table Dataset case
- Return type:
dict
- listAtt(tab=None)
Function to return a vector with the name of each column
- Parameters:
tab (text) – the table name in the multi-table Dataset case, defaults to None
- Returns:
a vector of names
- Return type:
vector of text type
- listAttRange(startIndex, endIndex, tab=None)
Function to return a subset of the names of a table
- Parameters:
startIndex (integer) – the starting index of the subset to consider
endIndex (integer) – the ending index of the subset to consider
tab (text) – the table name in the multi-table Dataset case, defaults to None
- Returns:
a vector of names
- Return type:
vector of text type
- listAttrValues(attr, valueRange, query=None)
Function to list the values of an attribute, eventually filtered, in a certain range
- Parameters:
attr (text) – the name of the attribute to consider
valueRange – a vector of integer of length 2. The first element is the starting index of the considered range, the second is the ending index of the considered range.
query (dict) – the matching criteria expressed as GOLD dictionary with the following key: - filterCriterion which assumes one of the following values (match, startswith, endswith, includes) - text equal to the matching string - words flag to force the matching string to match the whole word - caseSens flag to control if match has to be case-sensitive
- Returns:
the selected values
- Return type:
vector of text type
- listType(tab=None)
Function to return a vector with the type of each column
- Parameters:
tab (text) – the table name in the multi-table Dataset case, defaults to None
- Returns:
a vector of types
- Return type:
vector of text type
- load(ref='dataset', id=None, db=None, filepath=None, compute=False, table=None, onlysetglobal=False, alsodesc=False, inmemory=False, tables=None, onlyinfo=False, results=True, loadformat=True, leavememory=False)
Dataset class constructor
- Parameters:
ref (text) – the name of the underlying structure, defaults to dataset
id (text) – the id of the source where to load the structure (used in connection with param db to load the structure from a database)
db (Database) – a Database class, used in connection to id it is used to load the structure from a source on a database, defaults to None
filepath (text) – a path to a blob file which is used to load the underlying structure from the filesystem, defaults to None
compute (binary) – if True the dataset is loaded from the parent compute flow. Used only when the dataset is loaded as part of the computation of a Task, defaults to False
table (text) – the table name to select in case of multi-table load, defaults to None.
onlysetglobal (binary) – if True only the GOLD class wrapper is constructed without the underlying C structure, defaults to False
alsodesc (binary) – if True the column and metadata description is loaded from the underlying structure, defaults to False
inmemory (binary) – if True the whole dataset is load in RAM memory, defaults to False
onlyinfo (binary) – if True only column information are loaded and no rows, defaults to False
tables (vector of table names) – the list of tables to load in the multi-table case, defaults to None
results (binary) – if True also results columns are loaded, defaults to True
loadformat (binary) – if True styling format is loaded, defaults to True
- log(column)
Function to perform the natural logarithm on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated natural logarithm
- Return type:
vector
- log10(column)
Function to perform the 10 base logarithm on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated 10 base logarithm
- Return type:
vector
- lookUp(col, key, val)
Function to apply a look up table expressed as two vectors to a provided column
- Parameters:
col (column) – the column to be modified
key (vector) – a vector of keys to search for into the column
val (vector) – a vector of values associated to the provided keys containing the insertions to be done on the provided column
- Returns:
a resulting vector with each entry of column equal to some entries of keys substituted with the corresponing entry of val.
- Return type:
vector
- matchHeaders(column)
Function to fill a resulting vector in each row with the value containing in the column whose name is in the same row of a provided column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column filled with real attribute names used as filling rule
- Returns:
a vector filled with multiple values gathering by multiple columns
- Return type:
vector
- max(column, group=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the maximum of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns maximum is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the maximum of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the maximum row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated maximum is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- mean(column, group=None, weights=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the mean of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns mean is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the mean of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the mean row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated mean is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- median(column, group=None, weights=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the median of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns median is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the median of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the median row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated median is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- min(column, group=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the minimum of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns minimum is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the minimum of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the minimum row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated minimum is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- minute(time)
Function to extract the minute of a given datetime or time column
- Parameters:
time (column) – a datetime or time column
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted minute
- Return type:
vector of integers
- mode(column, group=None, weights=None, usemissing=False, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the mode of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns mode is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the mode of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the mode row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated mode is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- month(date, extract=False)
Function to extract the month of a given date column or to cast the original column to a month vector
- Parameters:
date (column of date type, defaults to None) – a date column
extract (binary) – if True the extracted vector is casted to GOLD month type, otherwise the integer month is given as result, defaults to False
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted month if extract is False, the month vector otherwise
- Return type:
vector of integers if extract is False, else vector of months
- movMean(column, leg, group=None, front=True)
Function to perform the moving Mean of a column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
leg (integer) – the range of rows of the moving window
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
front (binary) – if True the moving window is moved in advance, behind otherwise, defaults to True
- Returns:
the evaluated moving mean
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- moveAttribute(names, indexes=None, target=None, before=False, tab=None, keepresult=True, naux=-1, backup_index=None)
Function to move columns in a Dataset.
- Parameters:
names (vector of text type) – the names of the column to move
indexes (vector of integers) – if provided the final indexes of the columns to move, defaults to None
target (text) – if provided the name of the attribute with respect to moved columns will be placed of immediately before or after, according to before parameter. Not used in presence of indexes parameter, defaults to None
before (binary) – in connection with target it establishes if moved columns must be placed before or after the target column. Without the target column and the indexes parameter, moved the column before all the columns or after them, defaults to False
tab (text) – the table name in a multi-table Dataset case, None for the current one, defaults to None
keepresult (binary) – if True and some columns are moved right before first result they are still counted as result columns, defaults to True
naux (integer) – a number to force a number of result columns in the Dataset instance, -1 for no consider results, defaults to -1
backup_index – if provided the final indexes of the columns to move used only in case an attribute is specified in parameter target but it is not found in dataset, defaults to None
- multiplyRows(mult)
Function to duplicate any row of the Dataset a number of times as written in a selected column
- Parameters:
mult (integer) – multiplicity column containing the integer in each row about the number of times the row needs to be replicated
- nominal(var)
Function to cast a column to nominal type
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- numExt(column, onlyint=True, separator='-')
Function to extract all the numbers contained in a text
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to analyze
onlyint (binary) – if True only integer numbers are extracted, otherwise also continuous are considered, defaults to True
separator (text) – the separator to be used if more than one number is extracted, defaults to -
- Returns:
a vector containing all the numbers extracted, eventually concatenate using the separator
- Return type:
vector
- pad(column, len, value='0', where='begin')
Function to complete a text with a pad character until the text length does not reach a given threshold
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column of text type to be used in the operation
len (integer) – the final desired text length
value (text) – the character to be used as padding character, defaults to 0
where (text) – if begin the padding character is added at the beginning of the text, otherwise at the end, defaults to begin
- Returns:
the padded text
- Return type:
vector of text type
- pdf(column, *args, group=None, distr=None, **kwargs)
Function to evaluate the probability distribution function of a data column with respect to a particular distribution. Parameters for each distribution are: {“uniform” : [“min”, “max”], “gaussian” : [“mean”, “stdev”], “exponential”: [“beta”, “min”], “gamma”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “beta”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”, “max”], “cauchy”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “tstudent”: [“nu”, “mean”, “stdev”], “logistic”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “weibull”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “lognormal”: [“mean”, “stdev”, “min”], “chisquare”: [“nu”, “min”], “fdistr”: [“nu1”, “nu2”, “min”], “ksdistr”: [], “poisson”: [“lambda”],”binomial”: [“n”, “q”]}
- Parameters:
column (column) – the data column
args (list) – positional arguments used to define the distribution parameters
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
distr (text) – the distribution to use, None for uniform. One of uniform, gaussian, exponential, gamma, beta, cauchy, tstudent, logistic, weibull, lognormal, chisquare, fdistr, ksdistr, poisson, binomial, defaults to None
kwargs (dict) – keyword arguments used to defined the distribution parameters
- Returns:
the probability distribution function, eventually grouped
- Return type:
vector or group of continuous
- pearson(column1, column2, group=None, weights=None)
Function to perform the pearson between two columns
- Parameters:
column1 (column) – the first column considered in the operation
column2 (column) – the second column considered in the operation
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
weights (column) – a column to associate a possible weight to any column entry
- Returns:
the evaluated pearson or group of evaluated pearson
- Return type:
continuous or group of continuous
- percentage(var)
Function to cast a column to percentage type
- Parameters:
var (column) – the column to cast
- Returns:
the casted vector
- Return type:
vector
- perm(column, ordered=False)
Function to make a random permutation of a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to mix
ordered (binary) – if True the final vector is than sorted ascending, defaults to False
- Returns:
the mixed vector
- Return type:
vector
- phonetic(column, component='P')
Function to extract the phonetic component from a given text
- Parameters:
column (column) – the original text column
component (text) – the type of phonetic component to extract, use P for the primary component, or S for the secondary component, defaults to P
- Returns:
a vector composed by the extracted phonetic components
- Return type:
vector of text type
- prefix(column, value, last=False)
Function to take in an column the text part before a searched value, return the whole string if the value is not found
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column on which perform the prefix operation
value (text) – the value to be searched
last (binary) – if True the value is searched from the end, from the begin otherwise, defaults to False
- Returns:
the vector composed by all the prefixes
- Return type:
vector of text type
- prod(column, group=None)
Function to evaluate the product of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns product is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the product of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the product row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated product is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- quantile(column, quant, group=None, weights=None, mult=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate a quantile of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns quantile is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
quant (continuous) – the value of the desired quantile
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the quantile of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the quantile row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated quantile is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- quarter(date, extract=False)
Function to extract the quarter of a given date column or to cast the original column to a quarter vector
- Parameters:
date (column of date type, defaults to None) – a date column
extract (binary) – if True the extracted vector is casted to GOLD quarter type, otherwise the integer quarter is given as result, defaults to False
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted quarter if extract is False, the quarter vector otherwise
- Return type:
vector of integers if extract is False, else vector of quarters
- query(prefilter=None, postfilter=None, group=None, apply=None, sort=None, expand=False, view='all', rawform=False, filter=None, code=None, changefields=True, loadformat=True)
Function to perform a query. Order of the operation is prefilter, group, apply, sort, postfilter
- Parameters:
prefilter (text) – condition string to be performed as prefilter operation, defaults to None
postfilter (text) – condition string to be performed as postfilter operation, defaults to None
group (vector of text type) – vector of column names to be grouped
apply (list) – list of two elements: first the name of the column, second the name of the function applied. In case of multiple apply use a list of list of two elements, defaults to None
sort (list) – list of two elements: first the name of the column, second the ascending order flag. In case of multiple apply use a list of list of two elements, defaults to None
expand (binary) – if False property indrow of the Dataset instance is modified to select only the first row of each group, defaults to False
view (text) – the model set view on which query needs to be applied. One of all, training, test, validation, defaults to all.
rawform (binary) – if True some different format in the condition strings are allowed, defaults to False
filter (text) – DEPRECATED filter condition string for Rulex 4 back compatibility, defaults to None
code (text) – full query code for undo/redo operation, defaults to None
changefields (binary) – if True it updates the table information in multi-table case, useful to remember the query after table switching, defaults to True
loadformat (binary) – if True Dataset styling is re-evaluated after query execution, defaults to True
- rand(*args, n=None, seed=None, group=None, var=None, **kwargs)
Function which fill a column with random values following a specified statistical distribution. Parameters for each distribution are: {“uniform” : [“min”, “max”], “gaussian” : [“mean”, “stdev”], “exponential”: [“beta”, “min”], “gamma”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “beta”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”, “max”], “cauchy”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “tstudent”: [“nu”, “mean”, “stdev”], “logistic”: [“mean”, “stdev”], “weibull”: [“alfa”, “beta”, “min”], “lognormal”: [“mean”, “stdev”, “min”], “chisquare”: [“nu”, “min”], “fdistr”: [“nu1”, “nu2”, “min”], “ksdistr”: [], “poisson”: [“lambda”],”binomial”: [“n”, “q”]}
- Parameters:
args (list) – positional arguments used to define the distribution type and the distribution parameters. Distribution type must be specified as first positional argument, when it is not present uniform distribution with min = 0 max = 1 will be considered.
n (integer) – if greater than 1, returns a vector filled with n randomic numbers, None for all dataset displayed lines, defaults to None
seed (integer) – the seed of the random generator, None means a random seed, defaults to None
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
kwargs (dict) – keyword arguments used to defined the distribution parameters
- Returns:
the probability distribution function, eventually grouped
- Return type:
vector or group of continuous
- randGauss(n=None, seed=None, mean=0, stddev=1)
Function to retrieve a random number between 0 and a given n according to a gaussian distribution
- Parameters:
n (integer) – if greater than 1, returns a vector filled with n randomic numbers, None for all the displayed lines, defaults to None
seed (integer) – the seed of the random generator, None means a random seed, defaults to None
mean (continuous) – the mean of the gaussian distribution, defaults to 0
stdev (continuous) – the standard deviation of the gaussian distribution, defaults to 1
- Returns:
the random number or a vector of random numbers
- Return type:
continuous or vector of continuous type
- randLegacy(n=None, seed=None)
Function to retrieve a random number between 0 and a given n
- Parameters:
n (integer) – if greater than 1, returns a vector filled with n randomic numbers, None for all dataset displayed lines, defaults to None
seed (integer) – the seed of the random generator, None means a random seed, defaults to None
- Returns:
the random number or a vector of random numbers
- Return type:
continuous or vector of continuous type
- removeAttribute(name, tab=None, checkused=False)
Function to remove attributes
- Parameters:
name (vector of text type) – the names of the attributes to remove
tab (text) – the table name in a multi-table Dataset case, None for the current one, defaults to None
checkused (binary) – if True the attribute is not deleted and an error is raised if the attribute is used in any widget (Rulex Studio component), defaults to False
- removeRow(indrow, complement=False, remove_index=False, undodataset=True)
Function to remove a set of rows
- Parameters:
indrow (vector of integers) – the index of the rows to delete
complement (binary) – if True the parameter indrow is used to list the rows to maintain, defaults to False
remove_index (binary) – if True rows are also removed from the displayed rows if present, defaults to False
undodataset (binary) – if False action will not be recorded on the undo structure even if present, defaults to True
- removeTab(tabremove)
Function to remove a tab in a multi-table Dataset case
- Parameters:
tabremove (text) – the table to remove
- renameTab(oldname, newname)
Function to rename a table in a multi-table Dataset instance
- Parameters:
oldname (text) – the old name of the table
newname (text) – the new name of the table
- replace(column, oldvalue, newvalue, ntimes=0)
Function to perform a text replace on a given text column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column on which perform the replace operation
oldvalue (text) – the value to be replaced
newvalue (text) – the value to be inserted
ntimes (integer) – the number of occurrence of oldvalue in var which need to be replaced, 0 for all, defaults to 0
- Returns:
the replaced vector
- Return type:
vector of text type
- reset()
Function to reset an applied query on the Dataset instance
- reshapeToLong(widenames, othnames=None, nwideatt=1, seqwide=False, keepkeys=False)
Function to perform a reshape to long operation on the current Dataset instance
- Parameters:
widenames (vector of text type) – the name of the attribute in wide format to be considered
othnames (vector of text type) – the names of the other columns to be considered in the reshape operation, None for all, defaults to None
nwideatt (integer) – the number of wide attribute to be considered, defaults to 1
seqwide (binary) – FIXME, defaults to False
keepkeys (binary) – if True the position of the long attribute is creating maintaining the order of the provided wide attributes, defaults to False
- reshapeToWide(keynames, longnames, widenames, othnames=None, fillmiss=False, sparseorder=False, nonames=False, decidetype=False)
Function to perform a reshape to wide operation on the current Dataset instance
- Parameters:
keynames (vector of text type) – the names of the key columns of the Dataset
longnames (vector of text type) – the names of the attributes in long format which are going to control the name of the new column in wide format
widenames (vector of text type) – the names of the columns will be erased since they will be rewritten in wide format
othnames (vector of text type) – the names of the other columns to be considered in the reshape operation, None for all, defaults to None
fillmiss (binary) – if True a fill up and fill down operation is performed on the newly created columns, defaults to False
sparseorder – if True newly created column are created accordingly to the original position of the long column which has generated them. Otherwise newly columns are all created at the bottom of the Dataset, defaults to False
sparseorder – binary
nonames (binary) – FIXME, defaults to False
decidetype (binary) – if True a smart type recognition is launched on the newly created columns, defaults to False
- root(son, group=None, whichpath='min', separator='-', weights=None, operator='sum')
Function to evaluate the roots of a graph
- Parameters:
parent (column) – parent column defining the graph
child (column) – child column defining the graph
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
whichpath (text) – the root searched, min to obtain the nearest root, max to obtain the further away root, all to obtain all the roots connected by a separator, defaults to min
separator (text) – in case whichpath is all, the separator used to concatenate different roots, defaults to -
weights (column) – possible weights column to associate to each node of the graph, defaults to None
operator (text) – the type of operation to use in considering weights of connected nodes; possible values are sum or prod, defaults to sum
- Returns:
the vector or the group formed by the evaluated roots
- Return type:
vector or group
- rootDistance(son, group=None, whichpath='min', separator='-', weights=None, operator='sum')
Function to evaluate distance from the roots of a graph
- Parameters:
parent (column) – parent column defining the graph
child (column) – child column defining the graph
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
whichpath (text) – the root considered in distance evaluation, min to obtain the nearest root, max to obtain the further away root, all to evaluate the distance with respect to all the roots and to connect the numbers by using a separator, defaults to min
separator (text) – in case whichpath is all, the separator used to concatenate different root distances, defaults to -
weights (column) – possible weights column to associate to each node of the graph, defaults to None
operator (text) – the type of operation to use in considering weights of connected nodes; possible values are sum or prod, defaults to sum
- Returns:
the vector or group formed by the evaluated distances, eventually separator connected
- Return type:
vector or group of continuous, integer or text type
- round(column, nprecision=0)
Function to perform the rounding value on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
nprecision (integer) – number of decimal digits to retain in rounding operation, defaults to 0
- Returns:
the evaluated rounding value
- Return type:
vector
- save()
Function to make persistent a query executed on the Dataset
- second(time)
Function to extract the second of a given datetime or time column
- Parameters:
time (column) – a datetime or time column
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted second
- Return type:
vector of continuous
- setModelingSet(set)
Function to change the current model set
- Parameters:
currview (text) – the new model set to assign. One of all, training, test, validation, defaults to test.
- shift(column, shift, group=None, cyclic=False)
Function to shift the first len elements of a column by a fixed shift
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to be shifted
shift (integer) – the fixed shift, positive for right movement, negative otherwise
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
cyclic (binary) – if the shift should be performed in a cyclic way, defaults to False
- Returns:
the shifted vector or a group of shifted vectors
- Return type:
vector or group
- sign(column)
Function to perform the sign on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated sign
- Return type:
vector
- sin(column)
Function to perform the sine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated sine
- Return type:
vector
- sinh(column)
Function to perform the hyperbolic sine on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated hyperbolic sine
- Return type:
vector
- sort(column, ascending=True, store=True)
Function to perform an sort query
- Parameters:
column (text) – column name to be considered
ascending (binary) – the order of the sort, defaults to True
store (binary) – if True, resulting indrow will substitute the property indrow of the Dataset instance, otherwise it is returned, defaults to True
- Returns:
if store parameter is False, the resulting indrow is returned
- Return type:
vector of integers
- splitAttribute(string, substring=None, nchar=0, charlist=False, decidetype=True, fillmiss=True, checkused=False)
Function to split an attribute into several columns according to a selected criteria. Possible criteria are: - split with respect to a given substring - split after a given number of character each - split at the presence of any of the character containing in a given list
- Parameters:
string (text) – the name of the column to be splitted
substring (text) – if present split is performed with respect to this provided substring, defaults to None
nchar (integer) – if different from 0 split is performed every nchar characters, defaults to 0
charlist (binary) – if True split is performed considering the substring parameter as a list of characters rather than a unique string, defaults to False
decidetype (binary) – if True, a smart type recognition is launched on the newly created columns, defaults to True
fillmiss (binary) – if True, continuous separator are treated as a unique one and no internal all missing column is created, defaults to True
checkused (binary) – if True, the presence of the original column in widget input is checked and error is raised if column name is present (only Rulex Studio), defaults to False
- sqrt(column)
Function to perform the square root on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated square root
- Return type:
vector
- std(column, group=None, weights=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the standard deviation of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns standard deviation is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the standard deviation of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the standard deviation row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated standard deviation is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- store(id=None, db=None, destroy=True, table=None, force=False, label=None, setloaded=False, ref=None)
Method to store the modified Dataset on a working db or on the ispace of the flow to continue the computation
- Parameters:
id (text) – the id to use to store the blob on the working db (used in combinantion with db param), defaults to None
db (Database) – a Database instance to be used as working db, defaults to None
destroy (binary) – if True the Dataset instance is destroyed at the end of this function, defaults to True
table (text) – the table to store in multi-table case, defaults to None
force (binary) – if True the store on the working db is performed even if the Dataset has no active modification, defaults to False
label (text) – an alias for table, defaults to None
setloaded (binary) – if True the Dataset store can then be loaded again, defaults to False
ref (text) – the name of the internal structure stored, defaults to None
- storeFile(dirpath)
Function to store the Dataset instance of a file
- Parameters:
dirpath (text) – destination folder path where Dataset files will be created
- strip(column, value, where='both', ischarlist=True)
Function to strip a value from an column of text type from the beginning or from the end
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column on which perform the strip operation
value (text) – the value to be stripped
where (text) – if the value should be stripped from the beginning (begin), from the end (end) or from both (both), defaults to both
ischarlist (binary) – if True the given value text is considered as a list of character and any character is stripped separately
- Returns:
the stripped text vector
- Return type:
vector of text type
- suffix(column, value, last=False)
Function to take in an column the text part after a searched value, return None if the value is not found
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column on which perform the suffix operation
value (text) – the value to be searched
last (binary) – if True the value is searched from the end, from the begin otherwise, defaults to False
- Returns:
the vector composed by all the suffixes
- Return type:
vector of text type
- sum(column, group=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the sum of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns sum is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the sum of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the sum row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated sum is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- tail(column, nchar)
Function to take the last n characters of each text inside the provided column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column on which perform the tail operation
nchar (integer) – the number of characters to take
- Returns:
the vector composed by cut texts
- Return type:
vector of text type
- tan(column)
Function to perform the tangent on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated tangent
- Return type:
vector
- tanh(column)
Function to perform the hyperbolic tangent on a given column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the evaluated hyperbolic tangent
- Return type:
vector
- textConcat(column, separator=None, group=None)
Function to return the concatenation of the text contained in a column with a possible separator
- Parameters:
column (column of text type) – the original column of texts
separator (text) – the eventual separator to be introduced during text concatenation, defaults to None
- Returns:
the text concatenation
- Return type:
text
- textCount(column, substring)
Function to decode an encoded column. Encoding supported: base64, hex, url
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to be analyzed
substring (column) – the substring to be searched
- Returns:
the number of occurrences
- Return type:
vector of integer type
- textDecode(column, enctype='base64')
Function to decode an encoded column. Encoding supported: base64, hex, url
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to be decoded
enctype (text) – the encoding applied on the object; one of base64, hex or url, defaults to base64
- Returns:
the decoded vector
- Return type:
vector of text type
- textEncode(column, enctype='base64', alsoslash=False)
Function to apply an encoding to an original text column. Encoding supported: base64, hex, url
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column to be encoded
enctype (text) – the applied encoding; one of base64, hex or url, defaults to base64
alsoslash (binary) – if True also slash character is encoded, defaults to False
- Returns:
the encoded vector
- Return type:
vector of text type
- textExtract(column, startpos, endpos)
Function to extract a slice of a text
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column of text type to be considered in the extraction
startpos (integer) – the starting positon of the extraction
endpos (integer) – the ending positon of the extraction
- Returns:
the extracted vector
- Return type:
vector of text
- textLen(column)
Function to return the number of characters of each text inside an column
- Parameters:
column (column) – the column on which perform the operation
- Returns:
the vector formed by the number of characters of each text of the original column
- Return type:
vector of integers
- textSort(column, ascending=True)
Function to re-arrange characters of each value of a text column in ascending or descending alphabetical order
- Parameters:
column (column of text type) – the column to be sorted
ascending (binary) – if True sort is performed in ascending order, descending otherwise, defaults to True
- Returns:
the sorted vector
- Return type:
vector of text type
- textSplit(column, separator, decideType=True)
Function to enlarge the dataset and fill the column with the split of a given column with respect to a given separator
- Parameters:
column (column of text type) – the original column of texts
separator (text) – the separator to be used in the split operation
decideType (binary) – if True the resulting column is than smart casted by using the decideType function, defaults to True
- Returns:
an enlarged vector with all the strings splitted
- Return type:
text
- time(hour, minute=None, second=None)
Function to construct or convert a time column
- Parameters:
hour (column) – a integer column representing the hour of the desired constructed date, or a datetime or text column to be casted to time, defaults to None
minute (column) – in case hour is an integer, the minute integer necessary to construct the time, defaults to None
second (column) – in case second is an integer, the second continuous necessary to construct the time, defaults to None
- Returns:
the constructed time vector
- Return type:
vector of times
- transpose(userow=True, usecol=True, decidetype=True)
Function to perform a transpose on the current Dataset instance
- Parameters:
userow (binary) – if True attribute names become the new first column, defaults to True
usecol (binary) – if True the first column is used for resulting attribute names, defaults to True
decidetype (binary) – if True a smart type recognition is launched on each transposed columns, defaults to True
- type(column)
Function to return the type of a column as a string
- Parameters:
column (column) – the considered column
- Returns:
the text containing the type of the column
- Return type:
text
- variance(column, group=None, weights=None, forevery=(None, None, 0))
Function to evaluate the variance of a column or set of column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a column or a set of columns. In case of set of columns variance is performed row by row and parameter group is ignored.
group (column) – one or more columns to be considered to create a group and iterate the operation inside each group, defaults to None
forevery (list) – list to define a possible moving window to perform the operation inside a further group dimension constructed through a spanning range. List is composed by three element, possible all columns: the first is the date/datetime/time column which controls the moving window, the second is the lag of the moving window and the third is a possible offset to allow user to shift the starting value of the moving window, defaults to (None, None, 0).
- Returns:
if column parameter is a single column and group is absent it returns the variance of the column, if column parameter is a set of column it returns a vector of the variance row by row, if group parameter is present and column parameter is a single column a group of evaluated variance is instead returned.
- Return type:
any or vector or group
- warning(condition=True)
Function to report a warning with a message
- Parameters:
message (text) – the error message, defaults to None
condition (binary) – the condition to check to determine whether error should be raised, defaults to True
- warningGold(message)
Function to raise an warning if a provided condition is True
- Parameters:
condition (binary) – a condition string eventually containing columns
message (text) – the message to sent in case of warning
- week(date, extract=False)
Function to extract the week of a given date column or to cast the original column to a week vector
- Parameters:
date (column of date type, defaults to None) – a date column
extract (binary) – if True the extracted vector is casted to GOLD week type, otherwise the integer week is given as result, defaults to False
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted week if extract is False, the week vector otherwise
- Return type:
vector of integers if extract is False, else vector of weeks
- weekDay(date, mondaystart=True)
Function to obtain the day of the week as a number from 1 to 7
- Parameters:
date (column) – the column to analyze
mondaystart (binary) – if True Monday is associated with number 1, otherwise Sunday is associated with number 1, defaults to True
- Returns:
the day of the week expressed as integer
- Return type:
vector of integers
- year(date)
Function to extract the year of a given date column
- Parameters:
column (column) – a date column
- Returns:
the vector composed by the extracted year
- Return type:
vector of integers